- 89 Oxygen Levels While Sleeping Baby
- Oxygen Levels Below 89 When Sleeping
- Oxygen Level Chart
- 89 Oxygen Level
The human body can survive without food for approximately three weeks and without water for about three days. How long can you survive without oxygen? Only about three minutes. These statistics demonstrate just how essential oxygen is to human life and just how serious the effects of oxygen depletion in the body can be.


Many people in the United States live with chronically low oxygen levels in the blood. This condition is known as hypoxemia. There are a number of factors that can contribute to hypoxemia, and the condition may be acute as well as chronic. The complications of hypoxemia are potentially serious, but it can also be treated.
Download the jre 8u65 macosx x64 pkg file. Is it normal to have a sudden drop in oxygen levels, like down from high 90's to 70's within minutes without exertion? Are there any suggested.
- When the oxygen saturation falls below 89 percent, or the arterial oxygen pressure falls below 60 mmHg — whether during rest, activity, sleep or at altitude — then supplemental oxygen is needed.
- People who struggle with getting enough oxygen and maintain a lower normal O2 sat (say oxygen level 94), like those with COPD, asthma or other pulmonary disorder, often have a faster heart rate. Similarly, if you have high oxygen levels and always maintain an oxygen level 95 or oxygen level 96, your heart rate may rest a bit lower.
Two Similar Names, Two Different Conditions
Some people may get confused about the difference between hypoxemia and hypoxia. Although the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they are separate but related conditions. The word “hypoxia” literally means “lack of oxygen.” The term “hypoxemia” is more specific, meaning a lack of oxygen in the blood.
Some doctors and medical publications generally apply the term “hypoxia” to refer to low blood oxygen levels. However, it is more accurate to use the term “hypoxemia” to refer specifically to lack of oxygen in the blood and “hypoxia” to refer to lack of oxygen in body organs and other tissues.
89 Oxygen Levels While Sleeping Baby
Body tissues receive oxygen from the blood, so when the circulatory system is unable to pump enough oxygenated blood around the body or if the oxygen level in the blood is insufficient, these tissues do not receive enough oxygen and hypoxia occurs. Therefore, hypoxia is secondary to (that is, caused by) hypoxemia, and prompt medical treatment for hypoxemia may prevent hypoxia from developing.
Testing for Low Blood Oxygen
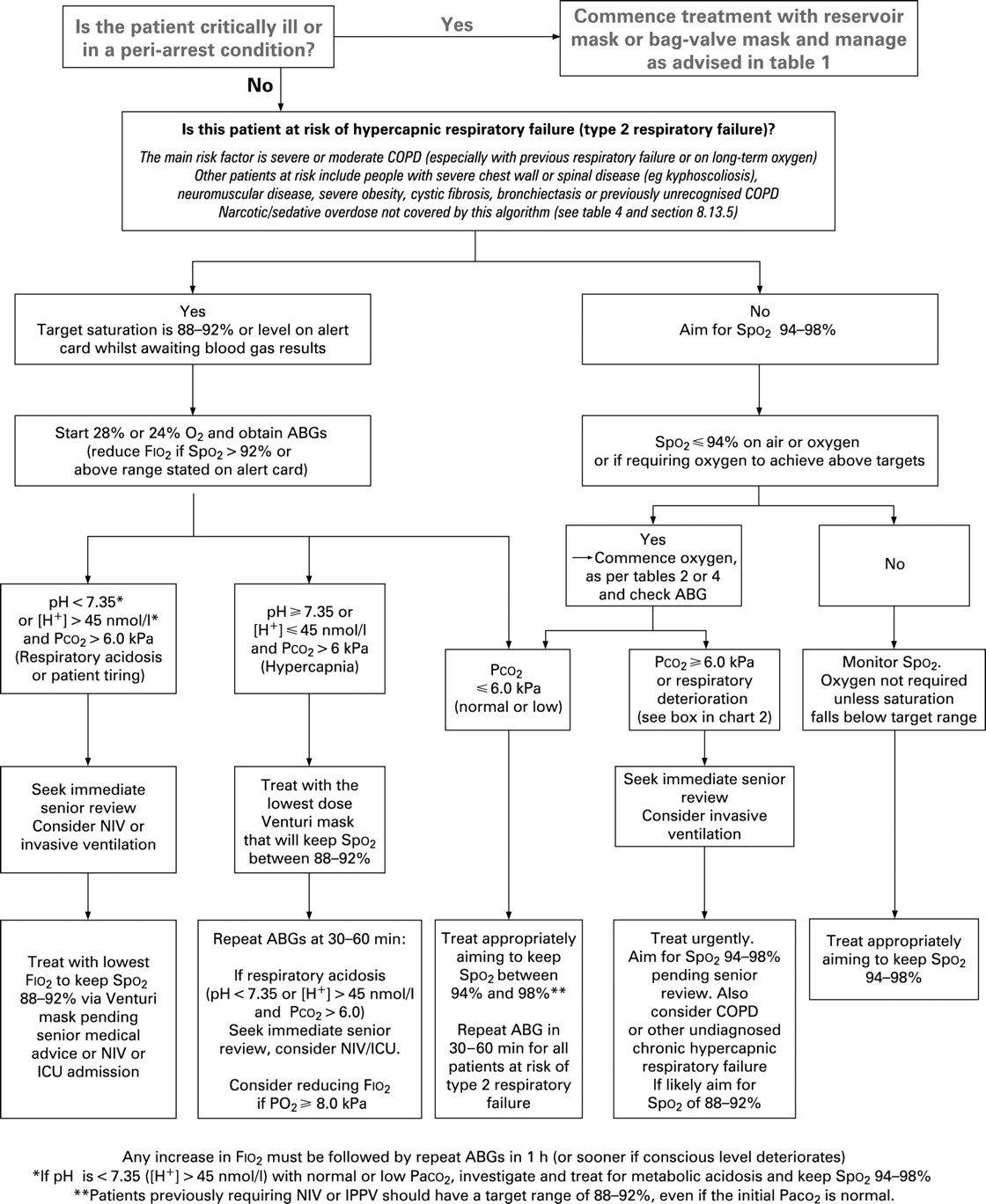
There are several methods used to test for low blood oxygen. If your doctor suspects that you have either hypoxemia or hypoxia, he or she may order pulmonary function tests. Many tests are included under this broad term, but they typically involve blowing air into a tube that is attached to a computer or other measuring device to discover how your lungs are functioning.
However, if the concern is that you may have low levels of oxygen in your blood, your doctor may choose to test your blood directly. There are typically two methods of doing this: a pulse oximetry test and a test of arterial blood gases. These tests may also be performed in addition to pulmonary function tests.
Your doctor will often perform a pulse oximetry test first. Pulse oximetry has many advantages over an arterial blood gas test. Pulse ox, as it is often known, is easy to administer and noninvasive. However, the trade-off is that it has a wider margin of error than an ABG. If your doctor suspects that your pulse ox results are not accurate, he or she may order ABG testing, which requires a sample of blood from the artery in your wrist, to confirm the pulse oximetry findings.
Pulse oximetry is measured in percentages: 95 to 100 percent is considered normal for a healthy individual, and anything below 90 percent is abnormally low. ABG is measured in millimeters of mercury. A range of 80 to 100 mmHg is considered normal for arterial blood gases in a healthy individual.
Causes and Symptoms of Low Blood Oxygen
There are essentially three basic factors that may cause your blood oxygen level to be low. A condition of the circulatory system may prevent your blood from reaching your body tissues. Cardiovascular conditions that may contribute to hypoxemia include congenital heart defects, or problems with the tissue of your heart that are present at birth. A congenital heart defect may be diagnosed in childhood or go undetected until you are an adult. Another potential contributing cause is anemia, or lack of iron in the blood. Oxygen molecules in the blood are transported by iron, so a lack of this element means the blood cannot pick up and carry the oxygen that the body needs.
Even if the circulatory system is functioning properly, hypoxemia may result if the lungs themselves cannot take in enough oxygen. Lung conditions that may result in low blood oxygen include the following:
Oxygen Levels Below 89 When Sleeping
- Sleep apnea
- Blood clot in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
- Emphysema
- Pneumonia
- Interstitial lung disease
Conditions that affect lung function may be acute, meaning they are severe and happen suddenly, or chronic, meaning they occur over time.
Hypoxemia can also result from a lack of oxygen in the atmosphere. This often occurs at high altitudes and can also result when the air is polluted by smoke or other contaminants. This type of hypoxemia may be acute and is often transient, meaning it goes away when the quality of the air improves.
Symptoms of hypoxemia can range in severity. The following are troubling symptoms that do not require emergency care but should be evaluated by a doctor as soon as possible:
Oxygen Level Chart
- Symptoms of sleep apnea (waking up short of breath or choking)
- Shortness of breath at rest or after slight exertion
- Shortness of breath that is worse with exercise
Dragon ball z tenkaichi tag team para ppsspp. The following symptoms require emergency care:
- A blue tinge to the skin or fingernails (cyanosis)
- Severe, acute shortness of breath that prevents functioning
- At high altitudes, shortness of breath accompanied by rapid heartbeat, cough, and retention of fluid
89 Oxygen Level
Treatment for Low Blood Oxygen
The treatment you may receive for low blood oxygen depends in part on what is causing it and whether it is acute or chronic. The first treatment usually administered for hypoxemia is administration of oxygen to increase the levels and prevent hypoxia from setting in. If the hypoxemia is acute, you may receive oxygen via a mask that fits over your mouth and nose, whereas if you require oxygen on a long-term basis, your doctor may prescribe oxygen tanks for you to carry around with you, and you’ll likely receive oxygen via a nasal cannula, a tube that inserts directly into your nose. Depending on what is causing the hypoxemia, it may be possible to treat with medications as well. Another major step you can take to prevent hypoxemia is to quit smoking and avoid breathing in second-hand smoke.
Low blood oxygen levels can have multiple causes as well as treatments. See your doctor to discuss options and work out the best individual plan to address your condition. T60m283 00 driver download.
Sources:
https://www.businessinsider.com/longest-survival-records-water-food-sleep-breathing-2016-5
https://www.healthline.com/health/normal-blood-oxygen-level
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/test_procedures/pulmonary/pulmonary_function_tests_92,p07759
https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/hypoxemia/basics/when-to-see-doctor/sym-20050930
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321044.php
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17727-hypoxemia
https://www.webmd.com/asthma/guide/hypoxia-hypoxemia#1

